1. Introduction
ocial networking sites (SNSs) are significant part of our lives in our society today;as a result, there is never a day that passes without its application, (Bozkurt, Karadeniz, & Kocdar, 2017) Users have enjoyed from this type of communication because of benefit they derived for example, the interactive and collaborative nature of the means of communication it offers (Faizi, Afia, & Chiheb, 2013). Research revealed that all over the world over 1 billion users are engaged in usage and this have propel researchers to continually involve researchers in conducting research on how people use the sites (Jin, Diego, & Chen, 2013;Subramani, 2015).
Thus there a lot of research interest on how international students also use the platforms available for their needs gartification (Rahman, 2014;Binsahl, Chang, & Bosua, 2015).
It is as a result of these availability and the engagement of usage that the present work tend to consider which networking sites do students prefer to use in EMU, North Cyprus and also to find out why they prefer some sites to others thereby considering the correlation that exist by nationality.
It is worth knowing that not communication online is now a days utilized as a single entity rather users are trying as much as possible to apply two or three for better results, while some are aimed at quaranteeing privacy sucha s Facebook, some like Instagram gives details using pictures with lots of attention from other, while some other prefer the use Twitter for intellectual stimulation, hence they are all aimed atsocial connection but having different communication modalities and such appeal to individuals in their own different ways (De Wall, et al. 2011;Hughes, et al. 2012).
Is not the availability but how students are managing their time to read and also the time they have for other things: the questions how often do they use the social media platform and which one do they frequently prefer to use since there are a lot of platforms. Based on this there may be some reasons that prompt them in choosing a platform to the other thus they are refered to as the reasons why people reduce their uncertainty if so how many platforms and the likely reasons for reducing their uncertainty.
2. II.
3. Objectives of the Study
4. a) History of Uncertainty reduction Theory
The uncertainty reduction theory was said to be theorized by Berger and Calabrese with the aimed at reducing any form of uncertainty in initial interaction theory in 1975 from the post-positive perspective, being the only theory that considers communication before engaging in a communication. This hinges on the fact that when people wants to interact they need some information about their interlocutor partners those information acquire will help them reduce their uncertainty about one another.
The Uncertainty Reduction Theory which is said to be initial communication in reducing doubt in communication based on the axiom posed by Berger and Calabrese, in an interpersonal communication is being utilized on SNSs too by users as buttressed that media users make use of media in an interpersonal way to satisfy their communication need ( Eginli &Tas 2018). Vijayalakshmi and Lawrence (2018), in an empirical studies emphasize that there is interpersonal relationship among middle age on social media with about 390 sample, which was related to different social networking platforms with the aim of ascertaining the impact of the use of platforms among students. This is because present communication is dominated by SNSs for interaction, collaboration and also regarded as the fastest means of communication which turns out to be a global means of communication, people cannot stay a day without using or applying it to their daily functions hence SNSs are inevitable in our daily lives (Yao & Cao, 2017;Luna & Pennock, 2018).
5. b) SNS and their different Historical background
The history of Social networking sites are believe to be in stages which can be traced back to the time that human begin to use the computer for their interaction (Linke, 2011). In 1997, the SNS began with the "sixdegrees.com" model which witness advancement in communication to be call (SNSs) this advancement, ease the manner people interact (Boyd & Ellison, 2007).
In supporting this, Chae(2018), observed that there are different SNSs with different functionality and applicability. Prominent among the sites are Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and Snapchat use for communication purposes, blogging and forming of communities as submitted by (Faruq, Rahman, & Alam, 2017). For example detailed information are done with Facebook, Pictures of things happening and other event are carried out with other platforms like snapchat and others.
WhatsApp are refered to as instant messaging thus, seen as secretive but very effective where users can upload, pictures and video,audio and also described as a selective instant messaging service for selected phones which can be connected to the internet hence its services are subscribe to, for smart phones and some selected phones with the features that WhatsApp, can be downloaded and function on This is confirmed by the Pew Research Center's Internet & American Life Project who chooses to examine SNS in a research to establish a fact that people all over the world depend on the use of social networking sites for their communication needs (Hampton, Goulet, Rainie, & Purcell, 2011).
All these are based on the gratification users derived from the use of their media. The Uses and Gratification Theory (UGT), consider how individual deliberately apply their media to fulfil certain needs. Some of the satisfactions users derive are itemize as: pastime, affection, fashion, share problems, sociability, and social information as given by (Quan-Haase & Young, 2010).
There are different reasons why people use specific media, while others are of the opinion that they use the Facebook to get in touch with friends some are of the opinion that they use it to pass time and to be entertained (Pempek, Yermolayeva, & Calvert, 2009). According to Ancu & Cozma (2009), their research revealed that users are after desire for social interaction, Information seeking and Entertainment on SNSs, while to Clark, Lee, & Boyer, (2009), SNS is use to be specific for passing time and meant to entertain.
In a recent research the use of SNSs was seen to be in different category in satisfying interpersonal need of connecting people, self discovery, entertainment value and social enhancement Ifinedo, (2016), thus we can say that SNSs are employed differently by different users and the users have choice of a platform.
In a similar vein, users also reduced their uncertainty using the SNSs too, as one of the means through which they can solve their problems as stated by Quan-Haase & Young, (2010). One of the uses and gratification obtain by user is to seek answer to those Ascertaining this by age, category among the students which group seems to be the avid users of reducing their uncertainty with a specific SNS, if more than one SNSs is put to use.
Secondly, age seems to be a factor that influences the choice of a network by preference, so the correlation between age and the preference will also be considered, since all the two nationalities use Facebook being the dominant of all the SNSs.
A lot of people have made some research inline the way people tend to prefer one network to the other but in Eastern Mediterranean University, there is little research with respect to case preference of a social media platform used by students, thus this will add to existing literature. For example, thesis on "Use of Social Media as an Alternative News Sources Among
6. c) Research Methodology and Design
The method use for this study is the quantitative research method which is based on measuring the strength in relationship between the variables. The questionnaires that were administered to the two nationalities were 310 but only 300 was successfully filled and returned with about 96.77% response rate.
The quantitative research methodology is said to be reliable because other researchers have employed this method in collecting data theses are:(Manasijevic, Zivkovic, Arsi, & Milosevic, 2016; Rousseau, Eggermont, & Frison, 2017). The research is aimed at conducting a survey on international students restricted to two nationalities (Nigerian and Palestinian) students in North Cyprus of their preference of SNSs by use.
7. d) Sampling and data Collection
Data were collected from 300 respondents studying at the Eastern Mediterranean University North Cyprus by using a probability sampling technique. Based on agreement from the Ethics committee, to carry out the research, the questionnaires were designed by the researchers. After administering the questionnaire it was collected back as they filled, the need to use the two countries is to give a reflection of not being restricted to a particular region hence Nigerians from Africa and the Palestinian from the Middle-East all in EMU, North Cyprus.
8. e) Measures
The questionnaire administered contains Demographics questions, Background information of the users. Others questions are those that concerns the users number of hours and reasons for using a particular social networking sites additionally the students level of uncertainty based on behavior exhibited on social networking sites were put into consideration and questions on their preference reasons for preferring a particular platform was also posed. 9-28 questions are divided into questions on Likert scale of use of platform, uncertainty and preference of a platform. Each group uses the Likert scales ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree on a scale of 5 points. And in all the questions posed to answer the questions are in statements form in accordance with (Froget, Baghestan and Asfaranjan 2013).
V.
9. Reliability and Validity
The computed Crombach alpha is at .818 and on standardized item, .837, thus meeting the required measurement scale as reliable to be qualified as given by Nunnally(1978) thus for the questions under preference on friendship and reduction of uncertainty, the result is seen on the tables below.
Considering table 1 below the questions are mixed with those on friendship and how their uncertainty in those relationship are establish and which one is most preferred. The outcome is the crombach alpha of each question, thus based on the table they can be used since it is quantitative results and can be generalized:
10. Data Analysis and Results
11. Graph as table 2 2018 survey
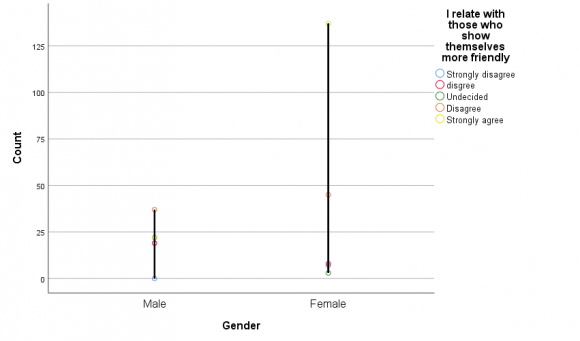
Data collected were analyzed with the help of the Statistical Package for Social Science version 25.Descriptive statistics were used to for the description of the samples and the Pearson's bivariate correlation, one-tailed significance criterion to determine the correlation of the variables age and usage for inferential statistics. Aside that, correlation for the two nationalities by preference, and that of level of uncertainty by gender, a one sample t-test (one tailed test) was used to ascertain if women reduced uncertainty more or their male counter parts Using point graph for the plotting friendship on social networking sites among international students in EMU, North Cyprus is based on how they show themselves friendly one to another. The number of men tend to be shorter as female dominate. On part of the female it depicts that the plotting is not directly on the lines which means it is not fully with strongly disagree but then also disagree to some extend that is not up to 10 counts that and below 50 also said they disagree and above 125 agree that students that show themselves friendly are those they relate with on side of the female respondents only since their points seems to be higher.
12. a) Ethical considerations
The research was guided and approved by the university Ethical Committee after fulfilling their requirement of submission of the consent letter to carry out a research on this topic, with the sample of the questions attached (reference number: ETK00-2019-0019) for the approval on the 21.02.2019. Participants were assured of the anonymity and the confidentiality of their rights and pre-inform of their willingness to withdraw from the study if they felt when they felt to withdraw.
13. b) Results
The result of the present study will be grouped into descriptive, Graph on points and inferential statistics to determine whether the questions posed are well answered based on this we can know the position of the questions if hypothesis posed can be accepted.
14. c) Descriptive results
Descriptive data analysis of the demographics respondents showed that age bracket between 22-27are the majority of the respondents with (n=159)53%, while age between 16-21 made up (n=81)27% and age 28-33 constitute (n=60)20%of the respondents. Based on gender more than half of the sample size are female constituting (n=200) 66.7% and the male are (n=100)33.3%.Regarding educational background, (n=225)75% for undergraduate while (n=75)25% for the graduate students. Lastly the result revealed that the majority of the respondents by Nationality are Nigerians (n=200)66.7% and Palestinians (33.3%, n=100).
With use of platforms as students the result reveal that the use of 2 platforms by students is the highest (n= 164, 54.7%), platforms (n= 74, 24.7%), the use of four platforms (n=42, 14%)while the use of one (1) platform, (n=20, 6.7%).
15. Number of
16. Field survey 2018
Results revealed that those who use more than one platforms are the majority about 164 out of 300 students use2 platform 54.7% and it is followed by students that uses 3 only with 74(24.7%) which is a clear indication that students have more than one social media platform for their communication for their gratification. On two different submissions Facebook as a platform is still leading in communication with about 85% and in place of business with 2 billion users making use of it as these two authors revealed with effect from January 1 to 10 that Facebook is still effective in all spheres (Ahmad 2019; Lua 2019). Based on the result above when all questions under preference are pull together they are given a name "preference of social media platform"( I prefer to use Instagram because it is Instant, "I prefer to use Facebook because you can write and share with other people," I prefer snapchat because you can snap and chat at the same time, Sometimes I use two to three platforms for my clarification, "I prefer to use Twitter because of less words, " I use LinkedIn as a professional, " I combined platforms because it reduced my uncertainty better, " On SNS I prefer to relate with my friends) "( ?= .751, M=3.93, all questions are on 5 Likert square, thus given "P"which is used to do the correlation and the since there are two items they are bivariate, result shows they nationalities and the preference of social media platform have positive correlation at 1 level of significant .000 is statistically significant at 2 tailed. Hence there is relationship between nationality and the user's preference of their social media platform.
17. VII. iscussion
Based on the question posed for this very research, result revealed that students will prefer to use more than a particular platform for their communication thus the use of at least two is the most preferred. This supports the notion that when there is high level of uncertainty information seeking behavior increases (AXIOM 3). See table 1a above.
Students are always willing to know something new based on research conducted in a school, results revealed that students use the different platforms based on their motivation thus they prefer one platform to the other therefore not using just 1 but 2 platforms, 3 platforms and 4 is an indication that students are inquisitive to source for information through other platforms (Alhabash and Ma 2017). See table 1a above too.
Correlation and the t-test sample shows that all nationality and preference of the platform are positively correlated and also age and level of uncertainty are significant statistically. Thus, the two based on inferential statistics they are positively related and also significant when computed.
Table 4 depicts some reasons for relationship to take place in other to reduce level of uncertainty, which the highest .776 "I relate with those that I think they can accept my friends request" which is faster.
Relationship usually is faster with those we think we know in a natural setting agreeing with the notion that for a relationship, " Results confirmed that Facebook as a platform which is agree to be the most popular of the platforms; facilitates spread-out social networks that grow excessively through distant kinds of relationship (acquaintances and activity connections), while also expanding the number of close relationships and stranger relationships, albeit at slower rates" (Manago, Taylor and Greenfieeld 2012).
Therefore since the place of uncertainty reduction is aimed at reducing uncertainty possibly it is worth knowing that the place of perceived Outcome value (POV) too is taken into consideration the rational steps of considering the goal during initial stage of meeting is targeted at interpersonal outcome, (Berger & Calabrese, 1975).
But the perspective of the POV individual at the beginning is for interactive friends to gain more information about their partner to enable them antedate the outcome in future interaction. In other words individual may choose to lay off the relationship if there is no need to have a close connection with their associates, (Sunnafrank 1986;1990). Consideration is given in the place of how to the conversational partners meeting and exchanging ideas that could open up for more interaction by way of information seeking thereby reducing uncertainty.
18. VIII.
19. Recommendation
This very research was conducted in an institution of learning therefore a similar research can be carried out in a work place where we also have different people of different background. Although the work took place in Turkish Republic of North Cyprus a replication the work can be conducted in Greece Cyprus to ascertain the result by nationalities that are there if it will yield same result. Additionally the need for longitudinal study to be conducted can also be carried out. More nationalities can also be used when next the researcher wants to conduct a similar research but with different nationalities.
| 25 | |||||
| Volume XIX Issue V Version I | |||||
| ( H ) | |||||
| Statement | Mean if item deleted | Scale Variance if Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Squared Multiple Correlation | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted |
| I relate with peers better because of age | 11.0167 | 9.749 | .598 | .361 | .790 |
| I reduced uncertainty | |||||
| based on pictures I see even if there is no | 11.1800 | 10.683 | .701 | .580 | .766 |
| word | |||||
| I relate faster with | 11.4167 | 7.929 | .615 | .385 | .806 |
| Number of platform used to reduce uncertainty | Frequency | Percentage |
| 1only | 20 | 6.7 |
| 2only | 164 | 54.7 |
| 3only | 74 | 24.7 |
| 4 and above | 42 | 14.0 |
| Total | 100.0 |
| Variables | Categories | Frequency | Percentage | |
| Age of respondents | 16-21 | 81 | 27.0% | |
| 22-27 | 159 | 53.0% | ||
| 28-33 | 60 | 20.0% | ||
| Total | 300 | 100.0% | ||
| Gender | Male | 100 | 33.3% | |
| Female | 200 | 66.7% | ||
| Total | 300 | 100.0% | ||
| Level of Education | Graduate | 75 | 25.0% | |
| Undergraduate | 225 | 75.0% | ||
| Total | 300 | 100.0% | ||
| Nationality | Nigerian | 200 | 66.7% | |
| Palestinian | 100 | 33.3% | ||
| Total | 300 | 100.0% | ||
| Depicting the reasons for reducing uncertainty for relationship to take place with the | ||||
| crombach alpha of each question | ||||
| S.No. | Statements on reducing uncertainty in relationship | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Cronbach's Alpha if Item Deleted | |
| 1. | I relate with those that I have had prior face to face contact | .564 | .762 | |
| 2. | I relate with those who show themselves friendlier. | .560 | .762 | |
| 3. | I relate with people based on lifestyle. | .649 | .730 | |
| I relate faster with people I think | ||||
| 4. | they can easily accept my friend | .546 | .774 | |
| request. | ||||
| 5. | I relate with my peers better because of age. | .605 | .746 | |
| (a): |
| Year 2019 |
| 27 |
| Volume XIX Issue V Version I |
| ( H ) |
| Global Journal of Human Social Science - |
| © 2019 Global Journals |
| One-sample Test | |||||||
| One-Sample Test | |||||||
| Test Value = 0 | |||||||
| 95% Confidence Interval of the | |||||||
| t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | Mean Difference | Difference | |||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Age | 48.935 | 299 | .000 | 1.93000 | 1.8524 | 2.0076 | |
| Uncertainty | 59.418 | 299 | .000 | 1.98571 | 1.9199 | 2.0515 | |
| Also on sample t-test results revealed that age | age and mean for uncertainty when computed is 2.00 | ||||||
| and level of uncertainty are significant. Therefore the | based on this it is significant. | ||||||
| degree of freedom is at 299 while the mean is 1.93 for | |||||||
| Correlation Analysis | |||||||
| Correlations | |||||||
| Nationality | Preference | ||||||
| Nationality | Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) | 1 | .687 ** .000 | ||||
| N | 300 | 300 | |||||
| Preference | Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) | .687 ** .000 | 1 | ||||
| N | 300 | 300 | |||||
| **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). | |||||||
| d) Inferential statistical results |
| Year 2019 |
| 28 |
| Volume XIX Issue V Version I |
| ( H ) |
| Global Journal of Human Social Science - |
| © 2019 Global Journals |